The GIHSN is supported by a dedicated fund, the Foundation for Influenza Epidemiology.
The Foundation for Influenza Epidemiology was created in September 2015 by Sanofi under the auspices of Fondation de France to formalize several years of commitment to epidemiological research on severe influenza.
This funding mechanism was established to facilitate additional funding from other donors for this world-scale active surveillance project.
Donors of the Foundation for Influenza include Sanofi, Seqirus, Abbott, Pfizer. Illumina and IFPMA contributed in previous years.
All donations collected through this foundation are dedicated to epidemiological research in the field of severe influenza and other respiratory viral diseases.
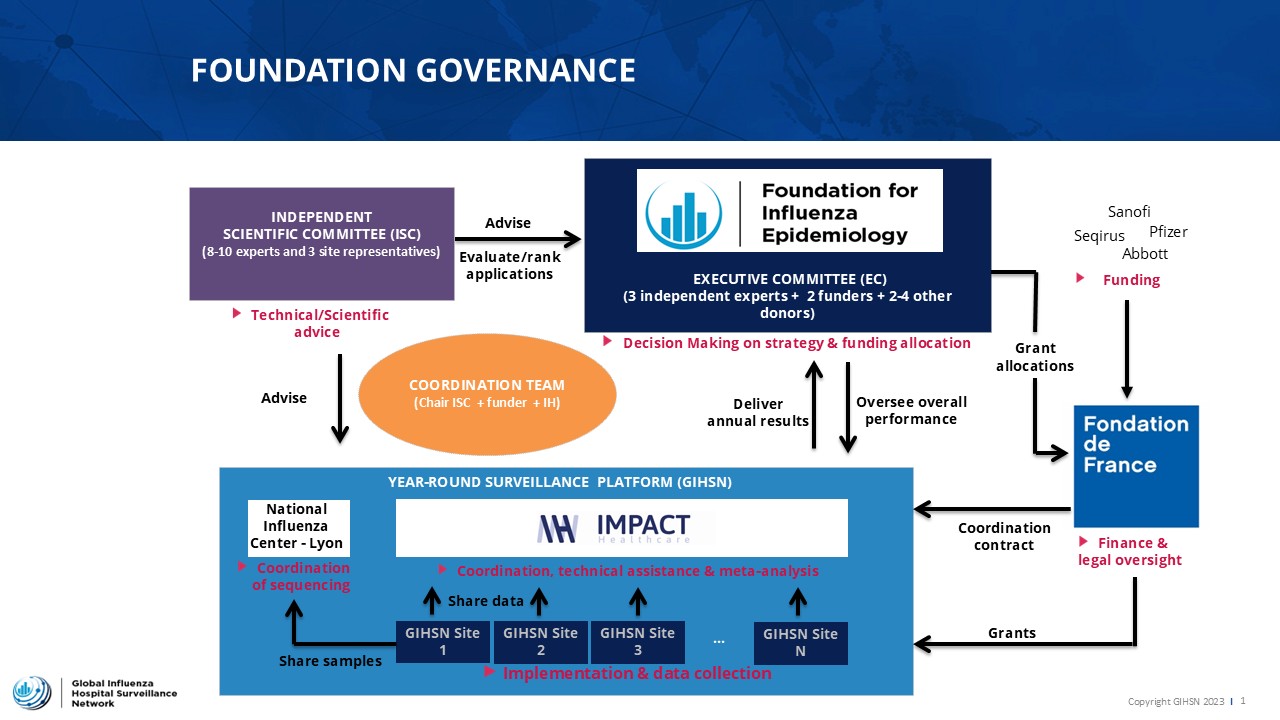
GOVERNANCE OF THE FOUNDATION
The governance of the Foundation for Influenza Epidemiology is ensured by an Executive Committee (EC). The Executive Committee is the decision maker, in charge of the strategic directions related to the project. Based on pre-established criteria, the Executive Committee selects applicant sites for funding allocation each year. The Executive Committee is composed of donors representatives and three independent experts.
Scientific oversight is ensured by an Independent Scientific Committee involving some of the world’s top flu epidemiology/virology/policy experts including representatives from US CDC and WHO.
Coordination of the network and operational implementation, including data collection & hosting, is supported by an independent organization: Impact Healthcare.
Members of the Scientific Committee
Independent Experts:
- Marta NUNES, CERP, University of Lyon, France (Chair)
- Bruno LINA, University of Lyon, France (former Chair)
- Joseph BRESEE, The Task Force for Global Health, USA
- John McCAULEY, Crick Institute, London, UK
- Justin ORTIZ, University of Maryland, USA
- Cecile VIBOUD, Fogarty International Center at the National Institutes of Health (NIH), USA
- Wenqing ZHANG, Global Influenza Program, WHO, Geneva (Observer)
- Sandra S CHAVES, Foundation for Influenza Epidemiology, France (Observer)
Site Representatives:
- Melissa K ANDREW, Canadian Serious Outcomes Surveillance Network, Halifax, Canada
- Sonia M RABONI, Virology Laboratory, Infectious Diseases Division, Universidade Federal do Paraná, Brazil
- Xavier LOPEZ LABRADOR, Virology Laboratory, Genomics and Health, FISABIO, Spain
*John PAGET (Netherlands Institute for Health Services Research, Utrecht) has been an important historical member
Cooperation with the World Health Organization (WHO)
The GIHSN is part of the WHO Mosaic Respiratory Surveillance Framework:
Presentation by Dr Wenqing Zhang, Head of Global Influenza Program, WHO “Continuously demonstrating complementary operations of various surveillance systems and partners”, November 2024
In October 2023, the Foundation signed a Memorandum of Understanding with the World Health Organization. Three key priority areas of collaboration have been highlighted:
- Virus co-circulation and alert mechanisms – GIHSN can provide useful information to describe a wide range of respiratory virus circulation at the level of hospitalized patients (case-based data vs. aggregated data). It can also potentially trigger an alert by identifying unexpected clusters of cases. Focus will be put on improving the timeliness of reporting, case-based reporting modalities, the potential for real-time reporting of some variables, and data reporting flow at the country, regional, and global levels. The expansion of the GIHSN (with the recruitment of new sites) will also be coordinated with WHO to ensure better geographical representativeness.
- Combination of severity and WGS for strain selection – Currently, some GIHSN sites without local capacities send samples for whole genome sequencing (WGS) to the Lyon NIC. WHO CCs and NICs may be able to support GIHSN sites by receiving specimens for WGS, increasing the volume of data and the timeliness of sequencing sharing to support decisions on strain selection for flu vaccines. The collaboration will focus on strengthening the link with NIC and WHO CC to perform more timely WGS and/or provide access to probes/reagents, develop further collaboration with GISAID, and potentially sequence other viruses (RSV, SARS-CoV-2, etc.).
- Burden of disease estimation and other research activities – In terms of research perspectives, the GIHSN relies on three pillars: a motivated and diverse community of researchers and clinicians; a hospital/lab infrastructure capable of conducting high-quality research; and rich, unique data generated every year. This infrastructure should be leveraged to address specific research questions, including the evaluation of catchment areas for burden of disease estimation, POC for preparedness, etc.


Comments are closed.